A Healthy Life with Comprehensive Cardiological Care
Introduction to Comprehensive Cardiological Care
In the pursuit of a long and healthy life, comprehensive cardiological care stands as a cornerstone. The heart, being the most vital organ, necessitates meticulous attention and care. Cardiological care isn’t merely about treating diseases; it’s about a holistic approach that encompasses prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management. This approach ensures that individuals not only survive but thrive, maintaining an optimal quality of life.

Understanding Cardiological Care
What is Cardiological Care?
Cardiological care is the medical discipline that deals with the disorders of the heart and circulatory system. This includes a wide range of conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and congenital heart defects. Comprehensive cardiological care aims to address these conditions through various means:
- Preventive Care: Emphasizes lifestyle modifications, regular screenings, and early detection of potential heart issues
- Diagnostic Services: Utilizes advanced imaging techniques, blood tests, and electrocardiograms to accurately diagnose heart conditions.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Includes medication management, surgical procedures, and innovative treatments like angioplasty and stent placement.
- Rehabilitation and Management: Focuses on cardiac rehabilitation programs, patient education, and continuous monitoring to manage chronic heart conditions effectively.
The Importance of Preventive Cardiological Care
Lifestyle Modifications
Preventive cardiological care starts with lifestyle changes. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding tobacco, and managing stress are crucial steps. These changes significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports heart health. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium can prevent hypertension and cholesterol.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
- No Smoking: Avoiding tobacco is one of the most effective ways to prevent heart disease. Smoking cessation programs can provide the necessary support to quit.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress contributes to heart disease. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can reduce stress levels.
Regular Screenings and Early Detection
Early detection through regular screenings can catch heart problems before they become severe. Blood pressure checks, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar tests are fundamental in identifying potential risks.
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Hypertension is a silent killer. Regular monitoring can help in early detection and management.
- Cholesterol Levels: High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries. Regular checks and dietary adjustments can keep levels in check.
- Blood Sugar Tests: Diabetes is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication can prevent complications.
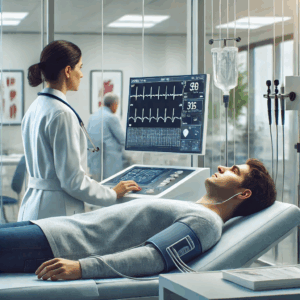
Non-Invasive Diagnostic Techniques
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A simple test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It helps in diagnosing arrhythmias and other heart conditions.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that provides detailed images, allowing doctors to assess the heart’s structure and function.
- Stress Tests: These tests evaluate how the heart performs under physical stress, helping to diagnose conditions like coronary artery disease.
Invasive Diagnostic Procedures
- Cardiac Catheterization: This involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart to diagnose and treat certain cardiovascular conditions.
- Angiography: X-ray imaging is used to see the heart’s blood vessels and identify blockages or abnormalities.
Therapeutic Interventions and Treatments
Medication Management
Medications play a crucial role in managing heart conditions. These include:
- Antihypertensives: To control high blood pressure.
- Statins: To lower cholesterol levels.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent blood clots.
- Beta-blockers: To reduce heart rate and blood pressure.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: Minimally invasive procedures to open blocked arteries.
- Bypass Surgery: Creates a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart.
- Pacemaker Implantation: Regulates the heart’s rhythm in cases of arrhythmias.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Management
Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehabilitation involves a personalized program of exercise, education, and counseling designed to help patients recover from heart attacks, surgeries, and other heart conditions.
- Exercise Training: Tailored to improve cardiovascular fitness.
- Education: On heart-healthy living and lifestyle modifications.
- Counseling: To address the psychological aspects of recovery.
Continuous Monitoring and Follow-Up
Ongoing care and regular follow-ups are essential in managing chronic heart conditions. This includes:
- Regular Check-Ups: To monitor heart health and adjust treatments as needed.
- Remote Monitoring: Using technology to track the patient’s condition in real-time.
- Patient Education: Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition and how to manage it effectively.

Comprehensive cardiological care is integral to achieving a healthy life. It encompasses preventive measures, advanced diagnostics, effective treatments, and ongoing management. By adopting a holistic approach, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and maintain a high quality of life. Emphasizing the importance of regular screenings, lifestyle modifications, and continuous care ensures that heart health is a priority, paving the way for a longer, healthier life.
Investing in comprehensive cardiological care today can lead to a heart-healthy future, allowing individuals to enjoy life to its fullest potential.